Progress in research and development of isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) inhibitors
December 27, 2017 Source: Yaodu Data
Window._bd_share_config={ "common":{ "bdSnsKey":{ },"bdText":"","bdMini":"2","bdMiniList":false,"bdPic":"","bdStyle":" 0","bdSize":"16"},"share":{ }};with(document)0[(getElementsByTagName('head')[0]||body).appendChild(createElement('script')) .src='http://bdimg.share.baidu.com/static/api/js/share.js?v=89860593.js?cdnversion='+~(-new Date()/36e5)];
Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH)
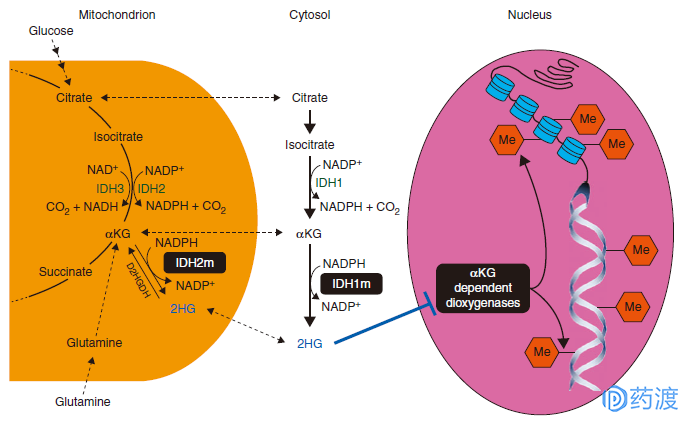
Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) is the rate-limiting enzyme involved in the energy metabolism of the drug, which catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of isocitrate to α-Ketoglutarate (α-KG). And CO2. There are three IDH enzymes in the human body, namely NADP-IDH1 in the cytoplasm, NADP-IDH2 in mitochondria and NAD-IDH3 in mitochondria.
IDH mutations are one of the causes of cancer in some tissues, and IDH1 and IDH2 mutations have been found in a variety of tumors, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML), glioma, chondrosarcoma, and cholangiocarcinoma. IDH mutations (IDH1m and IDH2m) in tumor cells cause loss of normal function and convert α-KG into the oncogenic metabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate (2HG), which accumulates in mutant tumor cells, resulting in DNA or group Protein is hypermethylated. By acting on the IDH mutation site in tumor cells, IDH inhibitors reduce the amount of oncogenic metabolite 2HG in vivo, thereby inducing histone demethylation and inhibiting tumor development. IDH inhibitors are classified into three types: IDH1 inhibitors, IDH2 inhibitors, and IDH1/IDH2 inhibitors depending on the target of action.
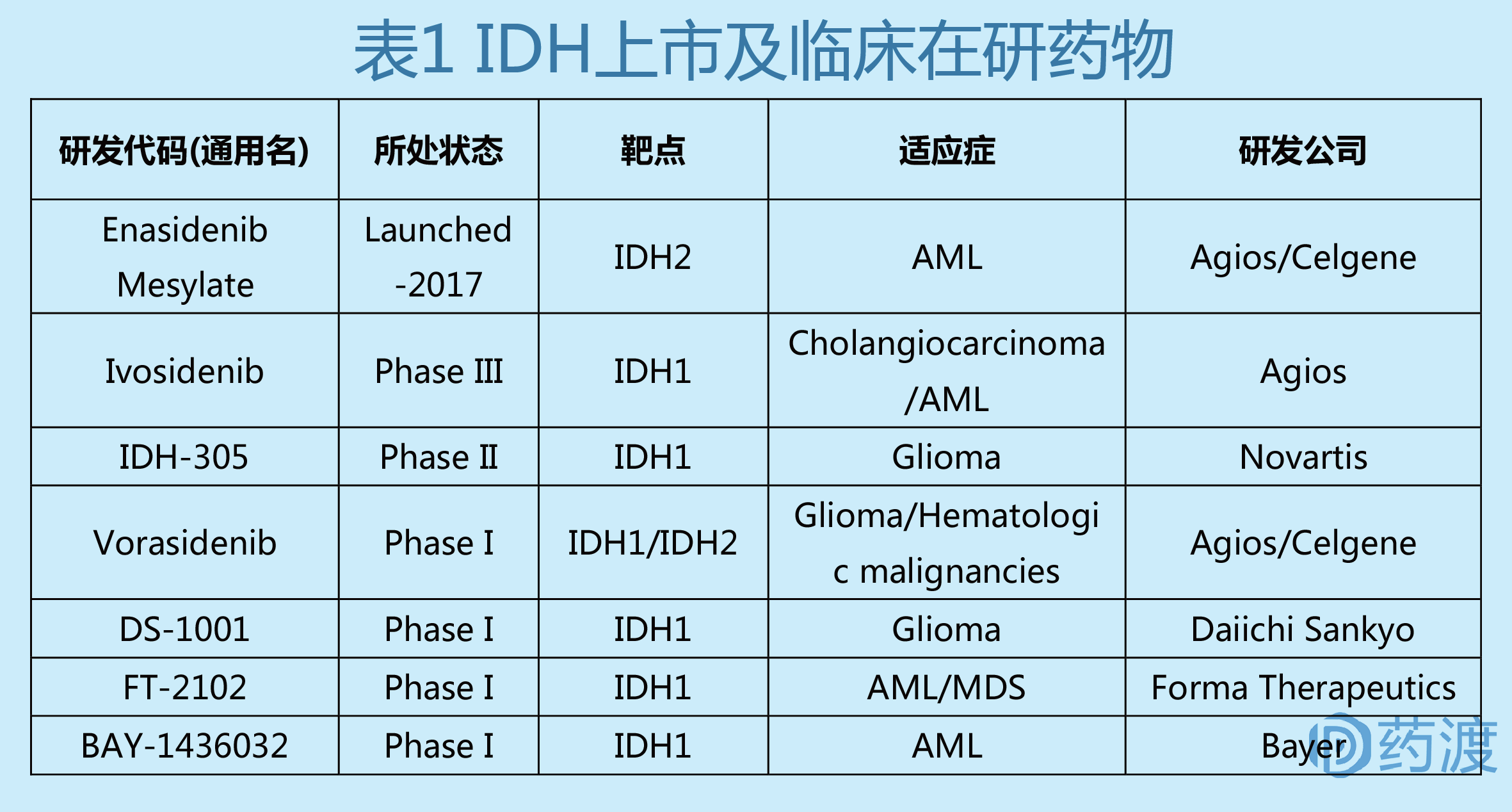
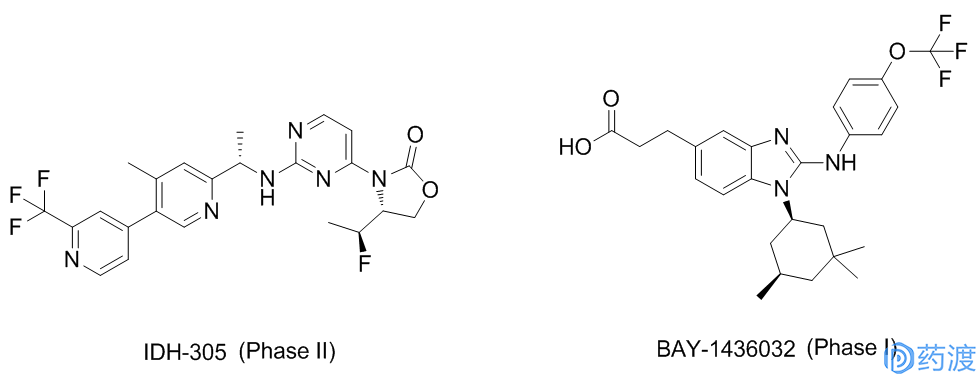
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a malignant disease of the hematopoietic system with rapid development and poor prognosis. According to the National Cancer Institute (NCI), about 21,380 people were diagnosed with AML this year, and 10,590 people will die of AML. In AML, approximately 8%-19% of patients carry IDH2 mutations that inhibit normal cell development. Glioma is the most common malignant tumor in the brain, accounting for 40%-50% of all intracranial tumors. The mutation frequency of IDH1 gene in secondary gliomas is more than 75%. Market demand determines the direction of research and development. Agios has pioneered the development of IDH1 inhibitors AGI-5198 (preclinical) and AG-120, IDH2 inhibitors AGI-6780 (preclinical) and AG-221, and IDH1/IDH2 inhibitor AG- 881. In addition, other companies and institutions have developed IDH inhibitors such as BAY-1436032, IDH-305, FT-2102 and DS-1001.
IDH action mechanism diagram
IDH2 inhibitor
Enasidenib Mesylate (AG-221)
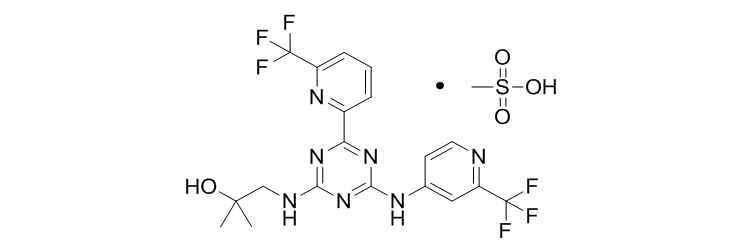
Developed by Celgene and Agios Pharmaceuticals, Enasidenib was approved by the US FDA on August 1, 2017 under the trade name Idhifa® for the treatment of IDH2 mutant, relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Enasidenib is the first IDH2 inhibitor and the first anticancer drug for tumor metabolism. It is reported that Agios started the project in 2009 and was introduced into the clinic in 2013. Due to the superiority of Enasidenib in clinical trials, the company was granted a rapid approval channel in August 2014 and was approved for listing four years later. Enasidenib has also entered the Chinese market and is currently conducting a clinical trial.
Enasidenib's approval is based on an open, one-arm, multicenter clinical trial (NCT01915498) in which 199 patients with relapsed or refractory AML carrying IDH2 mutations were recruited, and at least half of these patients had received 2 or more anti-cancer therapies. In the study, patients received an initial dose of 100 mg per day until the condition progressed or unacceptable toxicity. The results showed that approximately 19% (n=37) (95% CI: 13%, 25%) achieved complete remission (CR) with a median duration of remission (Median DOR) of 8.2 months (95% CI: 4.7). %, 19.4%); 4% (n=9) (95% CI: 2%, 8%) achieved partial hematologic remission (CRh) with a median duration of remission (Median DOR) of 9.6 months (95 %CI: 0.7%, NA). Of the 157 patients who required transfusion or platelets for AML, 34% were no longer in need of transfusion after receiving Enasidenib.
Enasidenib's Phase III clinical trial (IDHENTIFY; NCT02577406) is an international, multicenter, open, randomized clinical trial that began recruiting patients in October 2015 to demonstrate the effectiveness and safety of Enasidenib and traditional supportive therapies. In contrast, the primary clinical endpoint was overall survival (OS), which is currently underway.
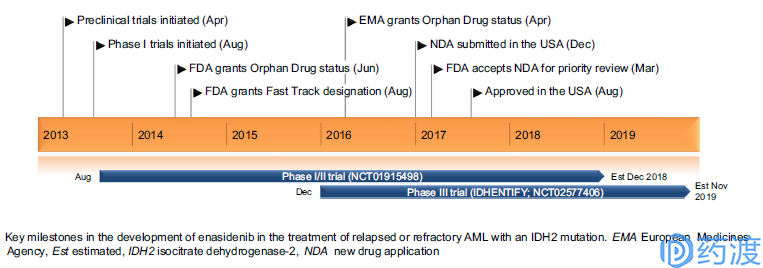
Enasidenib R&D Milestone
IDH1 inhibitor
Ivosidenib (AG-120)
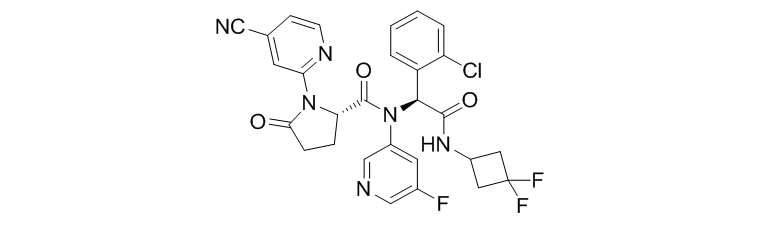
Ivosidenib (AG-120) is an IDH1 inhibitor developed by Agios Pharmaceuticals and is in Phase III clinical trials. It is intended to treat cholangiocarcinoma and relapsed, refractory acute myeloid leukemia. The US FDA has granted Ivosidenib orphan drugs and eligibility for rapid review.
In an early I/II clinical trial, the researchers enrolled 125 patients with relapsed or refractory AML. After receiving at least 6 months of treatment, the proportion of patients achieving complete remission (CR) or partial hematologic remission (CRh) was 30.4% (95% CI, 22.5%-39.3%), of which CR was 21.6%, CRh was 8.8%. In addition, the median remission period for these patients was 8.2 months (95% CI, 5.5-12.0), and the median remission period for complete remission patients was 9.3 months (95% CI, 5.6-18.3). The overall response rate (CR + CRi/CRp + PR + MLFS) was 41.6% (95% CI, 32.9%-50.8%). Good clinical trial data successfully promoted the drug to the clinical phase III.
In December 2016, Agios launched the Phase III trial of Ivosidenib for the treatment of IDH1 mutant advanced cholangiocarcinoma, a randomized, double-blind, parallel, placebo-controlled trial that enrolled 186 patients in the United States, estimated to be 2020 Completed in August.
It is reported that Agios plans to submit an NDA application to the US FDA at the end of 2017 for the treatment of relapsed and refractory acute myeloid leukemia.
IDH1/IDH2 inhibitor
Vorasidenib (AG-881)
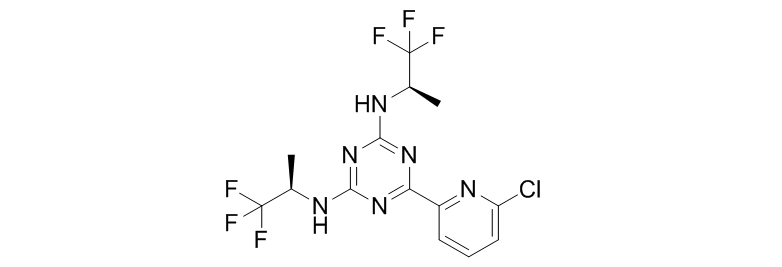
Vorasidenib is also a broad-spectrum IDH1/IDH2 inhibitor developed by Celgene and Agios Pharmaceuticals to inhibit both IDH1m and IDH2m. Currently in the first phase of clinical research, it is intended to treat malignant solid tumors (such as glioma) and malignant hematological tumors (such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS)).
Tumor metabolism therapy is a major research and development direction for cancer in parallel with immunotherapy, which indirectly inhibits tumor growth by reducing oncogenic metabolites. At present, the clinical safety data and validity data of isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) inhibitors are relatively optimistic, and it is expected to become a hot target for anti-tumor drugs.
references:
[1] Drugs@FDA
[2] Pharmacy data data.pharmacodia
[3] Enasidenib: First Global Approval
[4] IDH mutations incancer and progress toward development of targeted therapeutics
[5] Agios spotlights promising data for IDH1 drug, putting it on the path to FDA submission
Gelatin Empty Capsule,Hard Empty Gelatin Capsule,Bulk Empty Gelatin Capsule,Empty Gel Gelatin Capsules
Ningbo Jiangnan Capsule Co., Ltd. , https://www.ningbocapsule.com