Linkage between sample management and biopharmaceutical R&D processes – Mosaic sample management software
Marcus Oxer, Application Consultant, Titian Software Ltd.
Activity and efficacy screening are important steps in the development and final testing of biopharmaceuticals or biologics. Biological samples herein may include nucleic acids such as antibodies, enzymes, and the like, as well as small interfering ribonucleic acids (siRNAs). This screening is a very promising area as new technologies can screen out candidate molecules faster. But new technologies also bring new requirements and challenges, requiring screening and management of samples in shorter volumes and in higher throughputs (such as 384-well or even 1536-well microplates). This has forced users to pay more and more attention to the quality of sample management and the use of screening automation.
Why is efficient and accurate sample management important for macromolecular biological samples?
Production samples are often the result of skilled and intricate engineering activities. The active sample obtained by the primary screening marks the beginning of a large number of further characterization work, which is a highly skilled process. Therefore, recording the sample lineage is very important because the sample is transferred from one plate to the other, and the results of the analysis may be clearly correlated with individual samples in the tube or plate hole.
As the throughput increases, this problem will be even more difficult, requiring a sample management system that accurately tracks sample inventory and interacts with relevant automation equipment.
Biological sample management challenges
Sample registration
There is a comprehensive chemical registration system in the field of small molecule compounds, which is usually integrated with inventory systems such as Mosaic. Biological sample registration is not always done properly for the following reasons:
· Historically, production and biological sample/product screening has been processed at a lower level, which means lower demand for dedicated registration systems.
· The production or management of different biological products is not centralized and it is difficult to implement a single registration system.
· The rich diversity of biological products makes registration itself a complex challenge.
· There are fewer suppliers of biological sample registration services.
Even if there is a biological sample registration system, there is still a case of "not corresponding" to the existing category when registering a new item category because the diversity of biological samples is too large. The most common response (at least initially) is the management of spreadsheets (Excel). This is a big challenge for management teams that need to track unregistered samples. The Mosaic system has a flexible, built-in registration system that records virtually any conceivable sample type and can assign any number of custom fields to the system. This method can be used in conjunction with the chemical registration system and the biological sample registration system, and can be integrated with the above two systems. This provides a valuable means of quickly registering new type biometrics in the screening process as a temporary registry until the relevant samples can be registered in the relevant external system.
Unknown concentration
Typically, biological sample screening is primarily directed to the detection of activity (eg, affinity) during the initial screening process where the concentration is unknown. Concentrations were determined in subsequent rounds of screening, but for early screening, the system must also be able to cope with substances with "unknown" concentrations.
Experiment board layout and workflow
The discovery of a candidate drug may require several rounds of screening. For example, the culture supernatant is subjected to primary screening for Antibody activity, and then the active sample is placed in a new microplate for repeated screening. Samples may then be further selected and more analysis performed to quantify and further characterize the active sample. It may sometimes be necessary to culture a microplate containing biological samples of different dilutions. The Mosaic system can be integrated with automated liquid workstations to control liquid workstations to automate this liquid handling operation, managing complex experimental board layouts and nonlinear gradient dilution series. The layout of the board may vary depending on the type of screening (eg, the location of the control, standard, and blank groups), so a new layout needs to be easily configured. Similarly, the workflow may change, for example, the type of experimental instrument used for output, the number of copies required, and the like. With the Mosaic system, you can easily set up your analysis requirements and configure the new workflows you need.
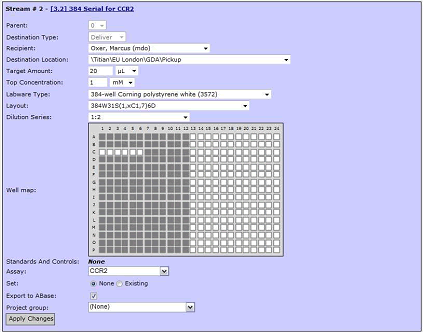
Figure 1 , Mosaic interface example - serial dilution of a special microplate layout
Shelf life, pollution
Typically, the biological product being tested is unstable at room temperature or may be degraded and degraded during the freeze-thaw cycle. This requires accurate tracking and recording of storage conditions during transport. Mosaic automatically counts the freeze-thaw cycle as it passes through the engineering stream. Another risk faced by biological products is microbial contamination, especially for culture supernatants, since culture supernatants are by definition in a nutrient-rich medium. This may require the liquid handler to be placed in a sterile environment, such as in a laminar flow hood, and its location may differ from other automated procedures. These are not a problem for the Mosaic system because it is designed to integrate with automation devices used in multiple locations.
Analysis result
After the test is completed, it is very likely that the layout information of the experiment board will be needed when analyzing the experimental results, and the microplate layout information in the Mosaic system can greatly speed up the calculation process. Depending on the sample type, the Mosaic system can export microplate layout information (substance, concentration, volume, and well location) to professional analysis software (such as IDBS's ActivityBase). For example, biological samples and small molecule compounds may require the export of different labels, concentration units, and the like.
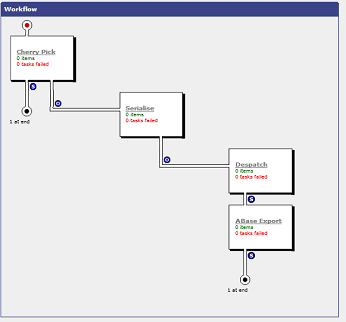
Figure 2 , Mosaic Command Workflow Example - AutoBoard View Exported to ActivityBase
A customer case sharing
In a recent customer case, due to the integration of organizational functions, its compound management team was asked to prepare an assay-ready assay plate for antibody screening. They found that in addition to preparing traditional small molecule compound experimental plates, they also needed to prepare a macromolecular compound experimental plate. In terms of liquid handling, the team was able to complete the layout requirements and concentrations required for the biological sample plate experiment, but only rely on manual loading and complex Excel spreadsheets, and also need to be programmed to control the liquid workstation. Since the team is already a Mosaic system user (for small molecule compound management), they once again found us and are ready to extend the Mosaic system to a test board that assists in the production and management of biological samples (antibody, siRNA) screening.
Enter and register
The antibody sample plate is initially supplied to the compound management group with a spreadsheet containing information about the antibody, but the antibody is not registered elsewhere.
The first step is to solve the problem of introducing antibody plate information into the registration system of the Mosaic system. This step is completed by configuring Mosaic's Labware Importer to identify Excel sheets containing relevant antibody information. After that, simply import the provided Excel spreadsheet to register both the antibody and the microplate involved in Mosaic. Like small molecule compounds, antibody samples coexist in the same Mosaic system, and Mosaic and external registration systems integrate seamlessly.
Workflow
The team created a new workflow for this task to manage the cherry pick and serial dilution of antibodies. These processes are built in accordance with existing standard workflow steps within the Mosaic system to help users define the various loading steps and target board layouts required. For example (below), some of the in-board layout is a gradient dilution in the order of Z-type concentration in 4 holes (Figure 3).
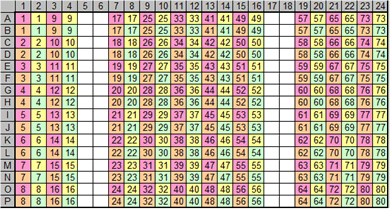
Figure 3 , 384- well Z -diluted microplate layout
Liquid category and liquid handling
Biological products are almost always in aqueous media. The liquid workstations of the Small Molecule Compound Sample Management Group are typically calibrated for DMSO based solutions. This makes a significant difference in the accuracy of the liquid handler. Therefore, by integrating with the instrument, the Mosaic system allows the workstation to automatically set the correct liquid category (for small molecules or biological samples) of the transferred substance type without manual intervention. This means that the team can manage all types of boards without any manual adjustments to the instrument. In addition, during dilution, the Mosaic system can prompt the operator to load a diluent suitable for the material being transferred.
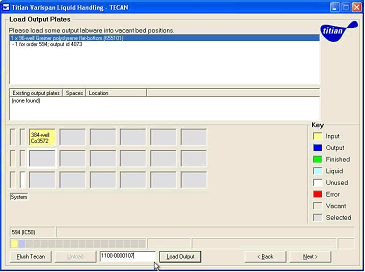
Figure 4 , Mosaic generates pipetting instructions and guides the operator
The Mosaic system can then instruct the liquid workstation to perform liquid processing and create a new experimental board using the workflow tools and processes that the team has set up. The layout information of the experiment board can be automatically exported to the ActivityBase analysis program to be associated with the screening result.
summary
Through the expansion of the Mosaic system, the project showed the following advantages:
· The fabrication of antibody microplates eliminates the need for complex manipulation of spreadsheets. Using the Mosaic system to direct and drive liquid workstations, any member of the sample management team can perform operations more easily and simply. This makes more efficient use of employee resources.
· Antibodies (or siRNAs) can be safely registered in Mosaic. Reduces the need to maintain Excel spreadsheets, and means that the Mosaic system can track the subsequent processing of biological samples.
· The sample management team now manages more sample throughput and ensures sample tracking accuracy.
· The responsibility for making biological sample screening panels can now be delegated to other teams, such as teams producing bioproducts, simply by integrating their liquid workstations with the Mosaic system. The workload can be shared between such different resources, and/or the cycle time between screening steps can be shortened.


For more information about Mosaic sample management software, please contact the China distributor as follows:
Tengquan Life Science (China) Co., Ltd.
Address: Room 211, 1133 Halle Road, Pudong New Area, Shanghai
phone
fax
e-mail:
Antibody
Ig M Antibody,Mycoplasma Igg,Antigen And Antibody,Igg And Igm
Guangdong Hecin Scientific, Inc. , https://www.hecinscientific.com