The continuous growth of horny horns is a normal physiological phenomenon. However, under the conditions of long-term feeding, the bulls lack exercise, and the horny horns are reasonably worn out. It is prone to hoof changes, hoof cracks and limb hoofs. Obviously, when standing difficult, it seriously affects the mining and climbing. If the prevention and treatment is not effective, the use of the bulls will be reduced, and even eliminated prematurely.
1 hoof disease
The Qinghai Provincial Livestock Improvement Center has been breeding breeding bulls for more than 30 years. In the actual work, the common bull hoof disease has hoof deformation and hoof lesions. Hoof deformation refers to the change in the shape of the hoof, unlike normal hooves. Hoof disease refers to the pathological inflammation that has occurred in the hoof, and the clinical manifestations of redness, swelling, heat, pain and dysfunction. Among them, the hoof is the most deformed, accounting for about 75% of the hoof disease. The hoof deformation causes the hoof load to be uneven, which leads to the occurrence of leg and foot disease. After the hoof disease occurs, the inflammation spreads to the hoof and the knee joint, due to joint swelling and hyperplasia. It can also cause changes in the shape of the limbs and directly affect the performance of the bulls. For the prevention and treatment of hoof disease, we mainly take the principle of prevention, treatment as a supplement, and prevention and treatment.
2 preventive measures
2.1 Regular hoof repair The brooding of the bulls is carried out twice in the spring and autumn. The hoof deformation and hoof lesions are immediately repaired and treated.
The hoof repairs are soaked in water beforehand or after rain. At this time, the hooves are soft and easy to trim; the bulls must be fixed before each hoof repair to ensure the safety of humans and animals; the hoof is determined according to the body shape. The degree of exfoliation, to prevent bleeding caused by over-cutting, can not be completely corrected at one time, re-repair at intervals of 1 to 2 months; when repairing hooves, try to cut the inside and the hoof as little as possible, so that the inner toe is as high as the lateral toe, so that the sole is bottom Tilt to the side of the shaft so that it is not easy to retain the dung grass and dirt between the toes. When the hoof is loaded, the area of ​​the hoof bottom can be increased as much as possible. Cattle after hoof deformation or hoof repair should be placed in a clean, hygienic and dry enclosure to prevent infection by pathogens.
2.2 Construction of reasonable sites, and regular disinfection of bulls for a long time living on the concrete floor, can cause excessive softening of horny horny skin, skin damage of limbs and joints. Causes local severe lesions or arthritis caused by secondary infection of pathogenic bacteria, which seriously affects the performance of the bulls. To this end, we transformed the ground of the enclosure into a three-soil sports ground. A rubber mat was placed on the concrete floor in the enclosure to ensure that the environment of the breeding cattle was flat, dry and free of debris, effectively reducing the occurrence of bull hoof disease. Regularly sterilize the pens, sports fields, and mining sites, and concentrate the manure treatment to maintain the hoof hygiene of the cattle.

3 treatment
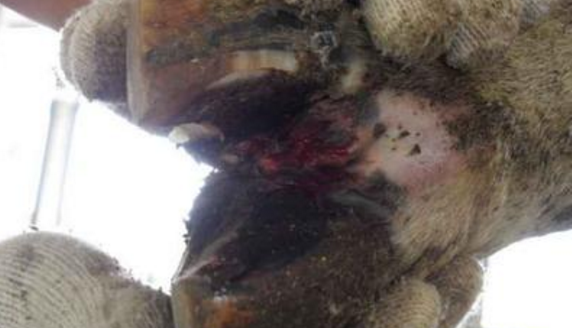
3.1 For limp and suspicious hooves, timely check and repair to check whether there is blood stasis, ulceration or necrosis at the bottom of the hoof. If there is, use a hoof knife to remove the abnormal tissue. Check if the sole is flat, whether the inclination is appropriate, whether the inside is upturned, whether there is a crack in the hoof wall, etc. If yes, correct it with a hoof knife or a hoof shovel.
3.2 Acupoint closure When the pain of the hoof is severe and the affected limb cannot reach the ground, it can be mixed with 2% procaine 5ml, penicillin 800,000 IU, streptomycin 1 million IU, and dexamethasone 5 mg. One injection every other day, combined with 3 times and combined with other treatments such as hoof repair, mild cases can be cured once with a single dose of medication. Heavier cases can be cured with 3 times of medication, which has the advantages of saving time, saving money and obvious curative effect.
For joints with soft swelling and severe pain, 50% glucose 50ml, vitamin B120.5mg, and dexamethasone 5mg can be injected into the joint cavity once a day, once every other day, with 2 times for special effects.
3.3 Trimming the hoof with a long hoof on the hoof, you can use the hoof repair tool to gradually cut off the hoof tip. To prevent bleeding caused by excessive repair of damaged dermal tissue, it is difficult to find a lesion on a wide range of cracks and rots at the bottom of the hoof. The proper thickness of the sole should be removed first to fully expose the lesion. After soaking the affected hoof with 4% copper sulfate solution, apply 10% fish fat ointment once a day for 3 to 5 days.
4 discussion
Bovine hoof disease is one of the common and frequently-occurring diseases of bulls, and it is one of the most important factors affecting the full performance and comprehensive benefits of bull production. The incidence of bull hoof disease is an important indicator reflecting the level of overall herd management. From the allocation of the infrastructure of the bulls, the supply of bulls to the full price of the diet, the daily management, the mining operation to the health and epidemic prevention and other technical links, all have direct or indirect impact on the occurrence of bull hoof disease. Therefore, in order to minimize the incidence of bull hoof disease and improve the utilization rate of excellent bulls, comprehensive prevention measures must be taken. We have received satisfactory treatment after years of practice.
colostomy pouch ostomy pouch stoma pouch urostomy pouch
Wenzhou Celecare Medical Instruments Co.,Ltd , https://www.celecaremed.com