The need for standardized testing of vitamin D
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble steroid derivative, which is mainly derived from dietary and ultraviolet light and is synthesized as an essential nutrient for the human body. Due to changes in human lifestyles (increased indoor living time, the popularity of sunscreen and sunscreen clothing) and their own causes (skin melanin content, skin vitamin D production decreased and damage increased), vitamin D deficiency is widespread worldwide, affecting 30%-50% of people [1] . In recent years, with the deepening of research on vitamin D, it is found that vitamin D deficiency not only causes imbalance of bone health, but also causes osteoporosis, falls and fractures, and is also closely related to various diseases such as cancer, muscle function disease, and cardiovascular disease. Disease, diabetes, immune system diseases, nervous system diseases, respiratory diseases, liver and kidney diseases, skin diseases [2,3,4] :
- 25(OH)D is the main form of transport of vitamin D in the blood. It is high in concentration and stable, and has a long half-life (2-3 weeks). It is considered to be an important indicator for measuring vitamin D status in humans.
- Rickets, osteomalacia, osteoporosis, chronic renal insufficiency, liver failure, hyperparathyroidism, pregnant and lactating women, history of falls / The elderly with low-invasive fractures should consider the nutritional status of vitamin D [5] .
- Serum 25 (OH)D is the main diagnostic basis for vitamin D deficiency, mild vitamin D deficiency and early rickets; vitamin D deficiency and vitamin D deficiency rickets should be prevented from the perinatal period, focusing on babies and continuing into adolescence [6] .
- The nutritional status of the fetal vitamin D depends on the maternal VD nutritional status; pregnant women should monitor the 25 (OH)D concentration 3 months after pregnancy [6] .
- Evaluation of vitamin D status by blood 25(OH)D can help reduce the incidence of breast cancer, colon cancer, prostate cancer, etc., and help detect the effect of bone metastasis of cancer tumors; blood 25(OH)D can be used as a predictor of breast cancer metastasis and An important reference indicator for prognosis [7] .
- If the plasma I-PTH level of patients with CKD is higher than the reference range, serum 25(OH)D levels should be measured at the first consultation. When the results are normal, periodic 25(OH)D levels should be monitored. Once the patient is supplemented with vitamin D, serum 25(OH)D levels should be monitored every three months [8] .
- Taking GCS patients are recommended for fall risk assessment, height and 25(OH)D measurements, assessment of initial and recurrent fragility fractures, vertebral fracture assessment, or spinal imaging studies [9] .
Progress in the standardization test kit for vitamin D in China
In recent years, vitamin D has become a topic of widespread concern. With the extensive implementation of 25(OH)D testing, clinical laboratory experts have found that the results of different testing methods are significantly inconsistent, and even affect the clinical diagnosis of vitamin D deficiency. To correct this, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Office of Dietary Supplements (ODS) and the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Ghent in Belgium have collaborated to launch the Vitamin D Standardization Program (VDSP) [10] .
The purpose of VDSP is to promote the standardization of 25(OH)D detection methods in all laboratories around the world, thereby improving medical safety and ensuring health for all. On this basis, NIH-ODS proposes four main objectives of VDSP: (1) standardize 25(OH)D detection methods built by various manufacturers and laboratories; (2) Standardize the use of the National Nutrition Health Survey 25(OH)D detection method; (3) Implementation of an internationalization study aimed at improving the performance of the laboratory 25(OH)D detection method; (4) Study and report the difference in results after 25(OH)D standardization.
In order to ensure the accuracy of the 25(OH)D test results, in 2010 NIH-ODS and CDC collaborated to establish a standardized certification process for vitamin D, and called on all manufacturers and laboratories to participate actively. The certification process is conducted in two phases. In the first quarter, 40 reference methods (JCTLM certified) sera are issued for calibration, ensuring traceability of the results of the manufacturer or laboratory self-construction method. Subsequently, 10 blind samples were issued quarterly for precision and accuracy assessment. Participants will be issued a certificate of accreditation in accordance with the requirements of the certification process four times in a row, and the validity period is one year. The re-certification is once a year. The performance verification standard for vitamin D is ≤ 5%, and imprecision ≤ 10%.
IDS's Addis® 25 Hydroxy Vitamin D Standardization Test Kit is part of and certified by Vitamin D Standardization (VDSP) and is the only enzyme-linked immunoassay kit in the world to achieve standardized traceability. The product was registered with the China Food and Drug Administration in 2007. It has been clinically sold in China for more than 10 years, and the sample size has exceeded 3 million. It has established a huge database in major hospitals and has become a field of vitamin D testing. leader of.
The kit has stable quality and good performance. The performance indicators are as follows:
- The calibrator is traceable to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) standard reference material SRM2972 [11,12] ;
- The sample size is small, only 10uL, suitable for serum or plasma samples;
- High sensitivity, according to CLSI EP17-A, the blank limit (LOB) is 3. 3nmol / L, the detection limit (LOD) is 6.8nmol / L, the limit of quantification is 12nmol / L;
- High specificity, verified by CLSI EP7-A2, free from interference with vitamin D binding protein, HAMA, biotin, total protein, total cholesterol, hemoglobin, triglyceride, bilirubin, etc., with 3-epi-25 (OH)D has no cross reaction;
- The linear range is 16.3~250nmol/L, covering the multiple medical determination levels of vitamin D deficiency, deficiency, sufficiency and excess.
In recent years, more and more manufacturers and laboratories have joined the ranks of standardized certification. However, in China, the standardization of 25-hydroxyvitamin D test results still has a long way to go, requiring the joint efforts of clinical experts, laboratory experts, manufacturers and related personnel. The Addis® 25 Hydroxy Vitamin D Standardization Test Kit is a “standardized†kit that has been used in China for more than 10 years and provides a reliable tool for clinical vitamin D testing with consistent quality and good performance.
References [1] Lavie CJ. Lee JH. Vitamin D and cardiovascular disease will it live up to its hype. J AM Coll Cardiol, 2011, 58(15): 1547-1556.
[2] Hart G R. Medical conditions associated with vitamin D deficiency and the clinical consequences[J]. Review, 2004.
[3] Holick M F. Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency [J]. 2007, 357(3): 266-281.
[4] Wei Zhaoyong, Wu Fengyun. Detection of serum vitamin D in patients with chronic liver disease and its significance [J]. Liver, 2012, 17(10): 753-754.
[5] Xia Weibo, Li Mei. Evaluation, Prevention and Treatment of Vitamin D Deficiency——Guidelines for Clinical Practice of Endocrine Society[J]. Chinese Journal of Osteoporosis and Bone Mineral Diseases, 2011, 04(2): 144-146.
[6] 2008 Vitamin D deficiency rickets prevention and treatment recommendations.
[7] Zhuang Zhigang, Yu Jianmin, Jiang Yiqi, et al. Determination and clinical significance of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in peripheral blood of patients with breast cancer[J]. Journal of Practical Medicine, 2010, 26(2): 244-246.
[8] Clinical Practice Guidelines for Bone Metabolism and Disease in Chronic Kidney Disease (KDIGO) (2009).
[9] 2010 American College of Rheumatology recommended for the prevention and treatment of steroid osteoporosis.
[10]https://ods.od.nih.gov/Research/vdspslm.aspx
[11]Sempos CT, Vesper HW, Phinney KW, Thienpont LM, Coates PM; Vitamin DStandardization Program (VDSP). Vitamin D status as an internationalissue: national surveys and the problem of standardization. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 2012Apr;243 :32-40.
[12] Thienpont LM, Stepman HC, Vesper HW. Standardization of measurements of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 and D2. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 2012Apr;243:41-9.
Peptone,Yeast extract,L-Glutamine,L-tryptophan,L-alanine,L-aspartic acid,L-methionine,L-threonine,Xanthan gum,Gellan gum,Bovine,serum albumin,Trishydroxymethylaminomethane,IPTG,Sodium pyruvate
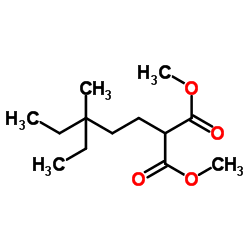
Peptone Basic Information
CAS: 73049-73-7
MF: C13H24O4
MW: 244.32726
EINECS: 615-895-9
Mol File: 73049-73-7.mol
Peptone Structure
solubility H2O: 50 mg/mL
form powder
color Dark cream powder
Odor Odorless
PH 6.5-7.5 (2% in H2O)
Water Solubility Soluble in water. Insoluble in alcohol.
Sensitive Moisture Sensitive & Hygroscopic
EPA Substance Registry System Peptones (73049-73-7)
Peptone,Yeast Extract,L-Glutamine,L-Tryptophan,L-Alanine,L-Aspartic Acid,L-Methionine,L-Threonine,Xanthan Gum,Gellan Gum,Bovine,Serum Albumin,Tris Hydroxymethyl Aminomethane,Iptg,Sodium Pyruvate
Shandong YingLang Chemical Co.,Ltd , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com