Hippo signaling pathway is a highly conserved growth control signaling pathway discovered in Drosophila in recent years, which plays a key role in regulating organ size, cell proliferation and apoptosis. This pathway is composed of a variety of tumor suppressor genes and a candidate oncogene. The inactivation or abnormal expression of this pathway is involved in the occurrence of various diseases in animal experiments.
The biological effects of the Hippo pathway include: regulating organ volume, maintaining cell proliferation and apoptosis, and maintaining internal environment stability;
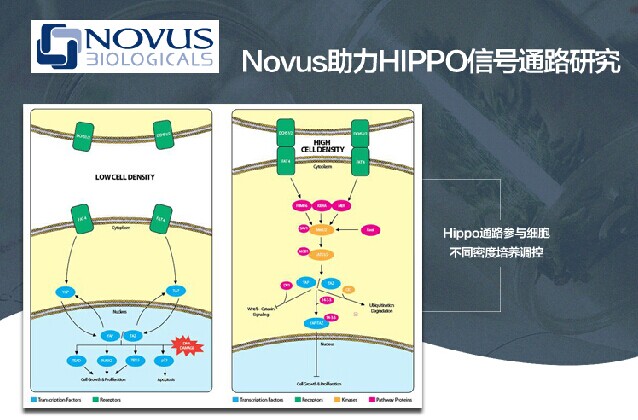
Involved in the regulation of cell contact inhibition, in cell culture, normal cells grow monolayer in culture concentration due to contact inhibition, and some tumor cells accumulate or anchor together rather than dependent growth due to loss of contact inhibition. ;
Inactivation of the Hippo pathway is involved in tumorigenesis: Hpo, Sav, Wts, Mats inactivation or overexpression of YAP are present in a variety of tumors, such as liver cancer, gastric cancer, colon cancer, prostate cancer, ovarian cancer, and the like.
In 1995, the first member of the Hippo signaling pathway, Wts, was found in Drosophila, which encodes a Dbf-2-related nuclear family protein kinase, a mutation in Wts that causes tissue overgrowth until 2002, in addition to the Hippo signaling pathway. Several members were also discovered, including Salvador (Sav), Hippo and Mats. The Hippo signaling pathway consists of core components, upstream and downstream components.
Core components: Lats1 and Lats2 are members of the Dbf2-related nuclear protein kinase family, which are homologs to Wts in Drosophila.
Upstream components: Several members are currently known as upstream components of Hippo and Wts. Atypical cadherin Fat acts as a receptor and participates in the regulation of Hippo signaling pathway. Transduction of Fat signal includes an unconventional muscle. Globulin Dachs, an overgrowth of Discs kinase, includes an adaptor protein Expanded (Ex) of the FERM domain, Ex is located in the apical region and is coordinated with another protein Merlin located in the apical region including the FERM domain. KIBRA is a WW domain protein that regulates the activity of the Hippo signaling pathway.
Downstream components, relatively few downstream genes involved in the Hippo signaling pathway, have clearly identified several downstream genes in Drosophila as Yki's target genes play an important role in organ growth, including miRNA, CyclinB and CyclinE, E2F1, and wither Death gene Apotposis-1. The human YAP gene is a homolog of Yki and has been discovered as an oncogene in some tumors. Recent studies have shown that YAP is the most primitive effector in the mammalian Hippo signaling pathway.
The Hippo signaling pathway does not play a single role, and the interaction of this pathway needs further study. It has been found that the Hippo signaling pathway is involved in the occurrence of a variety of human tumors, and the research on the mechanism of the disease involved is still to be deepened, so as to target the relevant therapeutic measures.
Novus provides a large number of high-quality antibodies against Hippo signaling pathway proteins, including core components Last1 and Last2, upstream components FAT, DACH, KIBRA, Merlin, and downstream component YAP, to help you more easily perform Hippo signaling pathway research.
Welcome to the Novus Explorer to find genes, diseases and references related to the Hippo pathway, please click: http://?start_mode=prefilled&entity_name=Hippo%20Signaling%20Cascade&entity_type=pathway
references:
1.Buttitta LA, Edgar BA. How size is controlled: from Hippos to Yorkies. Nat Cell Biol. 2007 Nov;9(11):1225-7. [PMID: 17975546]
2.Zeng Q, Hong W. The emerging role of the hippo pathway in cell contact inhibition, organ size control, and cancer development in mammals. Cancer Cell. 2008 Mar;13(3):188-92. [PMID: 18328423]
3. Badouel C, Garg A, McNeill H. Herding Hippos: regulating growth in flies and man. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009 Dec;21(6):837-43. [PMID: 19846288]
4.Varelas X, Miller BW, Sopko R, et al. The Hippo pathway regulates Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Dev Cell. 2010 Apr 20;18(4):579-91. [PMID: 20412773]
5.Bao Y, Hata Y, Ikeda M, Withanage K. Mammalian Hippo pathway: from development to cancer and beyond. J Biochem. 2011 Apr;149(4):361-79. [PMID: 21324984]
6.Zhao B, Tumaneng K, Guan KL. The Hippo pathway in organ size control, tissue regeneration and stem cell self-renewal. Nat Cell Biol. 2011 Aug 1;13(8):877-83. [PMID: 21808241]
7.Liu W, Wu J, Xiao L, et al. Regulation of Neuronal Cell Death by c-Abl-Hippo/MST2 Signaling Pathway. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36562. [PMID: 22590567]
For more information on HIPPO signaling, please follow: http://
Read the original text: http://
The so-called veterinary drugs, referred to as veterinary drugs, refer to drugs that can regulate the function of livestock from the body and prevent and cure livestock and poultry diseases. Natural plants, animals, minerals, and synthetic drugs and immunizations can all be used as veterinary drugs. Feed additives used in animal production are also often included in the category of veterinary medicines
Veterinary Drug,Hyaluronic Acid Powder,Oxytoci Acetate,Dmaa Powder
Shaanxi YXchuang Biotechnology Co., Ltd , https://www.peptidenootropics.com